1516 Legacy Cir, Naperville, IL 60563
How to Treat Periodontal Disease (Gum Disease)
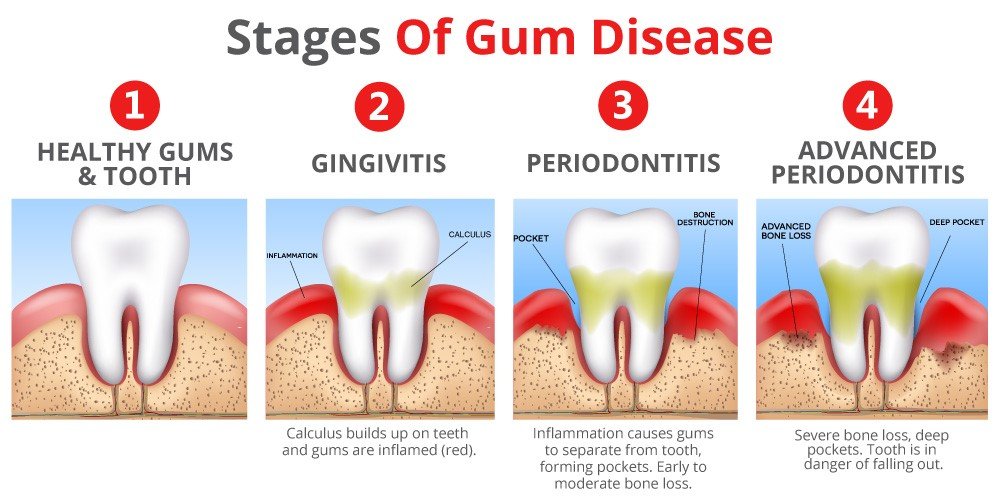
What is Periodontal Disease?
Unless you treat Periodontal Disease, you could experience the bacterial destruction of bone and soft tissue in the mouth. This condition is also known as gum disease or periodontal disease. The bone and gum tissue surrounding and holding the teeth in the mouth is compromised in people with periodontitis. Bone loss creates pockets around the teeth that fill up with bacteria. This bacteria continues to eat away at the bone, making the pockets increasingly deeper and increasing changes of tooth loss.
Loss of supporting gum tissue will also lead to eventual tooth loss. Periodontitis first starts as gingivitis. Gingivitis can be described as inflammation of the gum tissue caused by the bacteria in plaque and calculus. This condition is caused by poor oral hygiene and lack of professional dental cleanings, but can be reversed with proper brushing and flossing techniques at home and regular visits to the dentist. Once it progresses to periodontal disease, however, it is no longer reversible. Some patients may wonder, “is periodontal disease curable?” Unfortunately there is no technique on how to cure periodontitis, but there are many ways to treat it and maintain the remaining attachment levels.
How to Treat Periodontitis
Periodontitis can be treated with surgical and nonsurgical methods depending on how advanced the damage is. Dentists and hygienists will help guide patients towards the best options for how to treat periodontitis.
Professional Cleanings
The first step of action towards gum disease treatment is typically having a professional dental cleaning done by a dental hygienist. Patients with periodontitis are not good candidates for a “regular cleaning” because they have a disease process happening below the gumline.
Scaling and root planing, sometimes referred to as a “deep cleaning,” is the most appropriate periodontal disease treatment for patients who have active periodontal disease. This initial procedure is done for patients with active disease who have calculus deposits on the root surface of the teeth. The roots are smoothed out with special instruments used by the hygienist. By making the roots smooth, the likelihood the new bacteria will attach to them is lowered. This procedure takes longer than a regular cleaning appointment, and it might take more than one visit to complete.
Most patients will need to be numbed in order to keep the patient comfortable and for this cleaning to be completed to the best of the hygienist’s ability. Numbing can either be achieved with injections or a numbing gel that is administered below the gumline. Once the calculus and bacteria are removed, it is important that patients come back for maintenance cleanings. These are recommended at least three to four times a year because it is hard for patients to maintain periodontal pockets at home.
Surgery
Surgery is another option for more severe cases of periodontitis. Patients in need of periodontitis surgery are referred to a periodontist. This is a dental professional who specializes in gum disease, implants, and other procedures. Surgical procedures include bone grafting, gum grafting, flap surgery, and bone surgery.
Bone grafting is done to help regrow bone in areas with severe bone loss. The bone is either taken from the patient, a donor, or synthetic bone is used. Gum grafting is done for patients with gum recession. The tissue that is used to cover the area is most commonly taken from the roof of the patient’s mouth but can also be from a donor.
Flap surgery involves lifting the gums back and removing the tartar and irregular surfaces. After the roots have been cleaned the gum tissue is placed back around the tooth tightly so that the pockets are reduced in size. Sometimes a procedure referred to as guided tissue regeneration is done in conjunction with flap surgery. This procedure promotes growth of bone and tissue. A mesh barrier is placed so the tissue can grow where it is supposed to.
Lastly, bone surgery is done to recontour bone in a way that makes it difficult for bacteria to grow on. This is typically done after flap surgery.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics can be used to treat periodontal disease in conjunction with other methods to help maintain areas of bone loss in patients with periodontitis. They are often placed clinically to the sites immediately following scaling and root planing. Examples of these periodontitis antibiotics include doxycycline, tetracycline, and minocycline. There are methods for administering these antibiotics below the gumline at dental appointments. This has been proven to reduce the amount of bacteria in the pockets. Chlorhexidine is another agent used following scaling and root planing. Although it is not an antibiotic, this antiseptic treatment is beneficial for maintaining periodontal pockets.
Treat Periodontal Disease at Home
In addition to the in office treatments, it is important to stay on top of home care when periodontal disease is present. Patients with deep pockets should consider using oral hygiene aids such as water piks, proxy brushes, and electric toothbrushes. Patients with deep periodontal pockets will sometimes get food and plaque stuck in hard to reach areas. Water piks, also known as water flossers, are able to irrigate deep pockets that cannot be reached with a toothbrush or floss.
Proxy brushes, also known as interdental brushes, are perfect for patients who have lost gum tissue and have spaces in between their teeth. These brushes have a plastic handle with a wire and bristles at the end of it. They should fit easily in the spaces; forcing the brush into the space can cause more damage to the gum tissue. If the brush cannot fit in the space easily, a smaller brush size should be chosen. These are meant to be used once daily.
Lastly, electric toothbrushes are another great tool to treat periodontal disease at home. These can make a huge difference for all types of patients, but especially periodontal patients who are prone to developing calculus on their teeth. Electric toothbrushes can clean better than a manual brush because of the vibrations and spinning power of the brush head.
Periodontitis Treatment Benefits
It is important to address periodontal disease as early as possible because it will continue to worsen if left untreated. Untreated periodontal disease will eventually lead to tooth loss because there will be minimal attachment holding the tooth in place. Another reason to try to manage this condition early on is its effects on the body overall. Patients with active periodontal disease are more susceptible to other health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and low birth weight babies. If you think you are experiencing symptoms of gingivitis or periodontal disease, give our office a call to schedule an appointment!