1516 Legacy Cir, Naperville, IL 60563
How to Identify Root Canal Infection- Causes & Treatment
Root canal infections can be a painful and uncomfortable dental issue. They often appear unexpectedly, leaving individuals with questions about the causes, symptoms, and necessary treatments. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of root canal infections, helping you identify the reasons behind your discomfort and what steps to take to address it effectively.
What is a Root Canal Infection?
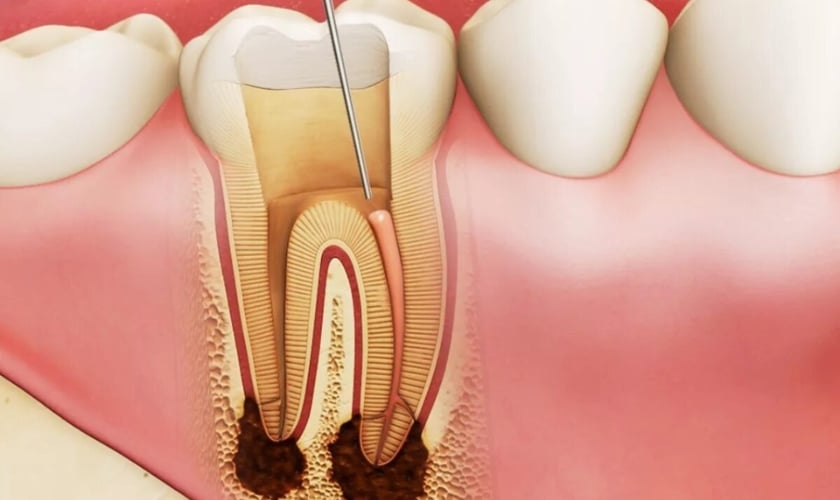
A root canal infection, technically known as endodontic infection, occurs when the pulp, the innermost part of your tooth, becomes inflamed or infected. The pulp contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue, and it’s crucial for tooth development and maintenance. However, when infection sets in, it can cause significant discomfort and, if left untreated, lead to tooth loss.
Why Root Canals Occur?
Root canal infections can happen for various reasons, but the most common causes include:
- Dental Decay: Bacteria that penetrate deep into the tooth can infect the pulp, leading to an infection.
- Trauma to the Tooth: An injury or trauma, like a sports injury or fall, can damage the tooth’s pulp and make it susceptible to infection.
- Cracked Teeth: Cracks in the tooth can expose the pulp to bacteria, causing an infection.
- Repeated Dental Procedures: Multiple dental procedures on the same tooth can weaken it, making it more prone to infection.
- Untreated Cavities: Neglecting dental cavities allows bacteria to reach the pulp and cause an infection.
Causes of Root Canal Infections
Understanding the specific causes of root canal infections is essential for effective prevention and management. Let’s take a closer look at these causes:
Dental Decay
Dental decay, also known as caries or cavities, is one of the leading causes of root canal infections. It begins when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the protective enamel of the tooth. This erosion progresses until it reaches the dentin (the inner layer of the tooth), and eventually, the pulp. When the pulp becomes infected, it leads to a root canal infection.
Trauma to the Tooth
Accidents or injuries that result in trauma to the tooth can damage the pulp directly or indirectly. Even if the damage is not immediately noticeable, it can weaken the tooth’s defences against bacteria, eventually leading to infection.
Cracked Teeth
Cracked teeth are particularly susceptible to root canal infections. These cracks can expose the pulp to bacteria and irritants, leading to infection. Cracks in teeth can occur due to a variety of factors, including biting down on hard objects, teeth grinding, or an injury.
Repeated Dental Procedures
Teeth that undergo multiple dental procedures, such as fillings or crowns, are more prone to root canal infections. Each intervention can weaken the tooth, making it more vulnerable to bacterial invasion. Sometimes, a root canal may be required after these procedures to address infection.
Untreated Cavities
Leaving cavities untreated is a significant risk factor for root canal infections. When a cavity is not filled, it allows bacteria to infiltrate the tooth, gradually infecting the pulp. Regular dental check-ups are crucial to identify and address cavities before they escalate into more severe problems.
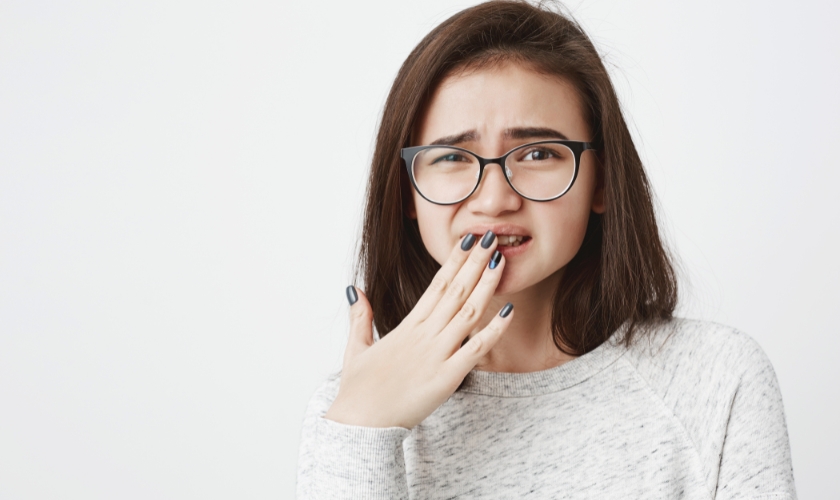
Symptoms of a Root Canal Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of a root canal infection is vital for timely diagnosis and treatment. Here are the common signs to watch out for:
Persistent Toothache
A persistent, severe toothache is often the most noticeable symptom of a root canal infection. The pain may vary in intensity, from a dull ache to a sharp, throbbing sensation. It typically worsens when you bite down on the affected tooth or apply pressure to it.
Sensitivity to Hot and Cold
If you experience heightened sensitivity to hot or cold foods and beverages, it may be a sign of a root canal infection. The affected tooth may react strongly to temperature changes, causing discomfort that lingers after the stimulus is removed.
Swelling and Tenderness
Inflammation and swelling in the gum tissue around the affected tooth are common symptoms of a root canal infection. You might also notice tenderness or discomfort when you touch the area.
Discoloration of the Tooth
A tooth affected by a root canal infection may change color. It can appear gray or dark yellow compared to your other teeth. This discoloration is a result of damage to the pulp and changes in blood flow to the tooth.
Abscess Formation
In more advanced cases, an abscess, which is a pus-filled pocket, may form at the root of the infected tooth. This can cause intense pain, and you may notice the formation of a pimple-like bump on the gum near the infected tooth.
Diagnosing a Root Canal Infection
If you suspect you have a root canal infection based on the symptoms you’re experiencing, it’s essential to seek professional dental care for a proper diagnosis. Dentists use several methods to confirm the presence of a root canal infection:
Dental Examination
Your dentist will begin with a thorough examination of your mouth. They will inspect the affected tooth, surrounding gum tissue, and any visible signs of infection or damage.
X-rays
X-ray images are a critical tool in diagnosing root canal infections. They can reveal the extent of damage, the location of the infection, and any abscess formation. X-rays are essential for planning the treatment.
Treatment Options for Root Canal Infections
Root canal infections require prompt treatment to prevent them from worsening and causing complications. The primary treatment options are as follows:
Root Canal Therapy
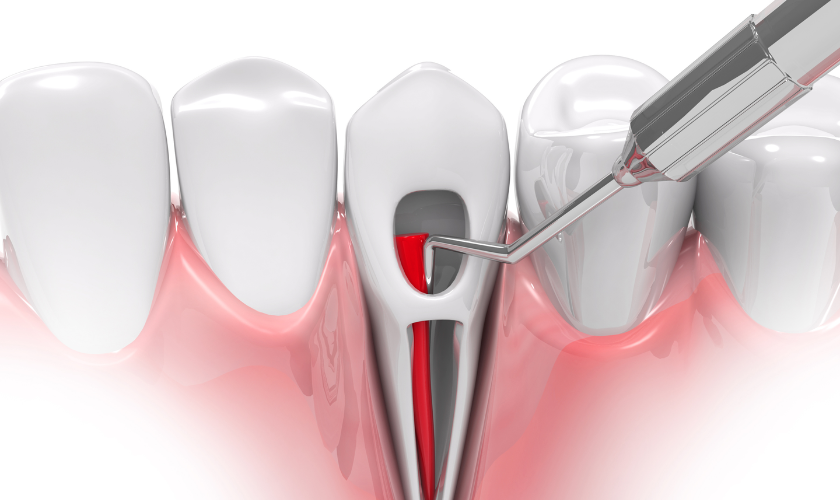
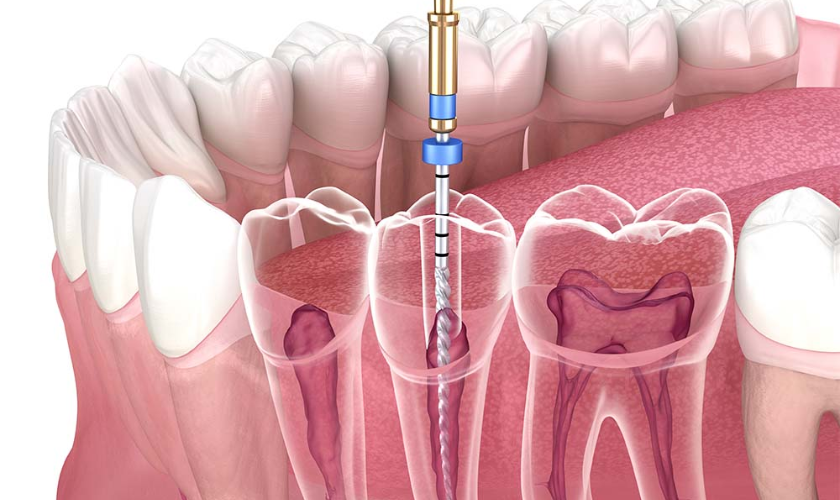
Root canal therapy, often simply referred to as a “root canal,” is the most common treatment for root canal infections. This procedure involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning the inside of the tooth, and sealing it to prevent further infection. Here’s an overview of the process:
- Anesthesia: The dentist will numb the area around the affected tooth to ensure you don’t feel any pain during the procedure.
- Access Opening: A small access hole is drilled in the crown of the tooth to reach the infected pulp.
- Pulp Removal: The infected pulp is carefully removed using specialized instruments.
- Cleaning and Shaping: The inside of the tooth is cleaned and shaped to prepare it for filling.
- Filling: The cleaned space is filled with a biocompatible material called gutta-percha, and the access opening is sealed with a dental restoration, typically a crown.
Root canal therapy has a high success rate and is often the preferred treatment for saving an infected tooth.
Preventing Root Canal Infections
Preventing root canal infections is the most effective way to avoid the pain and discomfort associated with this dental issue. Here are some preventive measures you can take:
Good Oral Hygiene
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is the foundation of preventing root canal infections. Follow these tips for good oral health:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen your breath.
- Replace your toothbrush regularly, approximately every three months.
- Avoid sugary and acidic foods, which can contribute to dental decay.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular visits to your dentist are crucial for early detection of dental issues. Your dentist can identify cavities and other problems before they progress to root canal infections. Dental check-ups typically include professional cleanings, X-rays, and a comprehensive examination.
Protective Measures
If you engage in activities that could put your teeth at risk, such as contact sports, wear protective gear like mouthguards to prevent trauma to your teeth. Additionally, if you grind your teeth at night, a dentist can provide a custom night guard to protect your teeth from damage.
FAQs About Root Canal Infections
Q: Can root canal infections heal on their own?
A: No, root canal infections cannot heal on their own. They require professional dental treatment to remove the infected pulp and prevent further complications.
Q: Is a root canal painful?
A: The procedure itself is performed under local anesthesia and should not be painful. However, you may experience some discomfort and mild pain in the days following the procedure, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
Q: Can root canal infections recur?
A: While root canal treatments are generally successful, there is a slight chance of reinfection if the tooth is not properly sealed or if new issues arise. Regular dental check-ups can help identify and address any concerns.
Q: Are there alternatives to root canal therapy?
A: In some cases, tooth extraction may be an alternative to root canal therapy. However, it’s typically recommended to save the natural tooth whenever possible, as extraction can lead to additional dental problems and may require replacement with a dental implant or bridge.
Identifying the causes and symptoms of a root canal infection is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. While root canal infections can be painful and uncomfortable, advancements in dentistry have made treatment highly effective, with a high success rate.
Remember that good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and preventive measures are key to avoiding root canal infections. If you do experience symptoms of an infection, don’t hesitate to seek professional dental care. Early intervention can help save your tooth and prevent complications.
If you suspect you have a root canal infection or want to learn more about dental health, schedule an appointment with your dentist today. Taking care of your oral health is essential for a pain-free and beautiful smile. Contact us to ensure the health of your teeth and gums.